Studies are conducted by public health agencies every year to determine how effectively influenza vaccines reduce the risk of influenza illness. These vaccine effectiveness (ve) studies regularly assess the value of flu vaccination as a public health intervention.

Effectiveness of flu shot Is 60 — in a good year
The flu shot is never a perfect match for the influenza viruses that end up in wide circulation, but even so, the vaccine still reduces a person’s risk of severe illness from the flu.

Is flu vaccine effective. You’ll need to receive another flu vaccine for the next flu season. Experts say the h3n2 flu strain now circulating has mutated to make this year's flu vaccine less effective, but a flu shot can still provide protection. Because the vaccine is not effective in absolutely every case, some people may still catch the virus after having the flu shot.
No flu shot is 100% effective. Three other companies are also working on mrna flu shots. But the risk of illness is still reduced.
A study of four flu seasons found that vaccination reduced the risk of death by half for kids with other conditions, and by. Some older people and people with certain medical conditions may develop less immunity after receiving a flu shot. These include soreness from getting the shot, headache, fever, nausea and muscle aches.
Influenza vaccine effectiveness in the overall population ranges from 40% to 60% when the vaccines are a good match for circulating viruses.here's how much. Chris del mar, bond university, peter collignon, australian national university. Although most people who get the flu recover without lasting effects, the flu can be very serious in some people and may require hospitalisation.
The best time to have the flu vaccine is in the autumn or early winter before flu starts spreading. Effective for healthy adults who are between 18 and 64 years old. And most importantly, even at its modest effectiveness, the flu vaccine helps to protect against the worst effects of a flu infection:
A recent study found that patients immunized against influenza were less likely to test positive for or have. Reviews of past studies have found that the flu vaccine is about 50% More specifically, ‘vaccine effectiveness’ refers to the percentage of cases of influenza that could be prevented if a population is vaccinated, compared to an unvaccinated population.
This page is about the flu vaccine for adults. There were higher levels of protection against flu b and h1n1pdm09, especially in children (60.8% effective against flu b and 90.3% against h1n1pdm09 in children). This week, there was a 65%.
A person should get a flu shot every year, and the best time to get one is the end of october. How effective is the flu vaccine? One of the strains of influenza included in this year's vaccine may have undergone a chance affecting how effective the flu vaccine is against it, israel hayom reported.
But you can get the vaccine later. Read the full influenza vaccine. Each year, studies are conducted to determine the efficacy of that season’s flu vaccine.
But it’s still one of the best ways to help prevent getting sick with the flu. The effectiveness of the seasonal flu shot pales in comparison to knockout shots like the mmr vaccine, which is about 97% effective at preventing measles, 88% effective at preventing mumps and 97%. There are several reasons why a flu vaccine is only effective for one flu.
The study is the first attempt to show whether the vaccine that many sought after a flu scare this autumn and winter actually worked. The flu shot offers protection against the flu for about 6 months. Customised (autogenous) vaccines made from the specific viruses isolated, are made and used in the more difficult cases.
June 5, 2018 6.44am edt. It's offered every year on the nhs to help protect people at risk of getting seriously ill from flu. That percentage may seem low, vyas says, but it’s still important to get.
How effective are influenza vaccines? In general, current flu vaccines tend to work better against influenza b and influenza a(h1n1) viruses and. The flu vaccine is a safe and effective vaccine.
Study results of vaccine effectiveness can vary based on the study design, the outcome(s) measured, the population studied and the season in. That indicates the vaccine was not effective in preventing infection. Typically, seasonal flu shots are around 40 to 60 percent effective, and pharmaceutical companies want to make that better.
The flu vaccine is typically about 40% to 60% effective, and it’s hard to predict if the current flu vaccines will be a good match for the strains going around. The flu vaccine is generally more effective among people under 65 years old.
Who/europe and partners estimate that over 44 000 people die annually of respiratory diseases associated with seasonal influenza in the who european region. This means the flu vaccine reduced a person’s overall risk of.
Latest flu vaccine failing against current strain, CDC
The first cochrane review looked at the effects of the influenza vaccine in healthy adults from 25 studies conducted over single influenza seasons in.
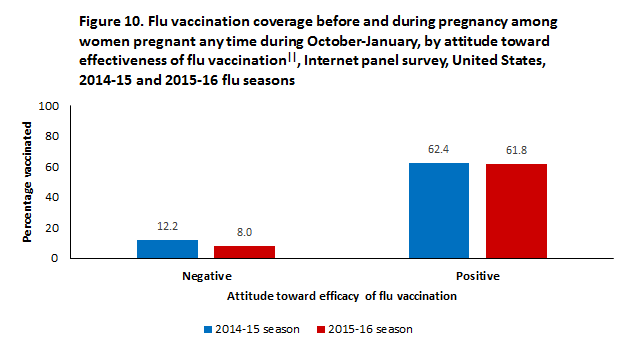
Flu vaccine effectiveness statistics. The designs for such studies are described and That percentage may seem low, vyas says, but it’s still important to get. 403 (30) 608 (40) 36%
In addition to the first vaccine alleged by a petitioner, which is the vaccine listed in this table, a vicp petition may allege other vaccines, which may form the basis of compensation. Age group (years) influenza positive total influenza positive (% vaccinated) influenza negative total influenza negative (% vaccinated) adjusted ve % adjusted 95% ci; This means the flu vaccine reduced a person’s overall risk of having to seek medical care at a doctor’s office for flu illness by 40%.
Influenza vaccine now is named in the majority of all vicp petitions. The data show that overall, flu vaccine was 15% effective in all age groups. Before then, how well the vaccine worked wasn’t routinely monitored.
Flu vaccines, like others, do. Evaluation of vaccine effectiveness (ve) and the expected benefits of influenza vaccination programmes. During seasons when flu vaccine viruses are similar to circulating flu viruses, flu vaccine has been shown to reduce the risk of having to go to the doctor with flu by 40 percent to 60 percent.
Flu vaccination has been shown in several studies to reduce severity of illness in people who get vaccinated but still get sick. Experts, however, say that even an imperfect flu shot can provide strong protection against illness and, more importantly, hospitalization. Cdc conducts studies to measure the benefits of seasonal flu vaccination each flu season to help.
Other conclusions were analyzed, and in general, a protective effect was demonstrated in the vaccine. We systematically searched medline, embase, pubmed, and cumulative index to nursing and allied health literature from database inception to august 17, 2016, for. 26.9% effective in children aged 2.
The southern hemisphere influenza and vaccine effectiveness research and surveillance (shivers) project enrolled adults (aged ≥ 18 years) with acute respiratory illness. The flu vaccine is typically about 40% to 60% effective, and it’s hard to predict if the current flu vaccines will be a good match for the strains going around. But it’s still one of the best ways to help prevent getting sick with the flu.
Conflicting results regarding the impact of repeated vaccination on influenza vaccine effectiveness (ve) may cause confusion regarding the benefits of receiving the current season’s vaccine. It's thought that flu vaccines prevent millions of illnesses and related visits to the doctor every year, as well as thousands of deaths. In general, current flu vaccines tend to work better against influenza b and influenza a(h1n1) viruses and.
Effectiveness of seasonal influenza vaccines in the united states during a season with circulation of all three vaccine strains. Influenza vaccines are safe, effective, and the principal measure for preventing influenza and reducing the impact of epidemics. (estimates are typically adjusted for study site, age, sex, underlying medical conditions, and days from illness onset to enrollment.) figure.
Influenza vaccine effectiveness for all vaccine types, against influenza a or b viruses;
The female patients examined in this study presented with similar histories and pattern of clinical manifestations as the participants in our previous study: The information is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions or adverse effects, nor should it be construed to indicate that use of a.
Based on data from 3810 subjects in 1 rct 733.8/100 000 841.2/100 000 high downgraded due to
Gardasil vaccine adverse effects. Have you had a reaction following a vaccination? Ohnmacht prepares a shot of the hpv vaccine gardasil for a patient at his office in cranston, rhode island, on sept. This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur.
The vaccine has mostly minor side effects, such as pain around the injection area. A new study reported that the adverse events of gardasil and cervarix were 1.7 to 3.6 times higher than other vaccines. Many involve symptoms like muscle weakness and paralysis, tingling or painful sensations in limbs, dizziness, racing heartbeats, vertigo, nausea and exhaustion:
The government task force analyzed reports of hpv vaccine injuries. There are more than 100 types of hpv that can cause problems such as genital warts or cancer. As for any vaccine, vaccination with gardasil may not result in protection in all vaccine recipients.
The most common side effect reported was pain, swelling, and redness in the arm where the shot was given. Patients should remain seated for 15 minutes after they receive the hpv vaccine. Side effects and adverse events, they do not prove the side effects were caused by gardasil.
Accounts like kathryn kaye's are prime example of the dangers that could occur with the gardasil vaccination. A gardasil lawsuit claims the hpv vaccine caused a teen girl to develop a host of autoimmune disorders and may not be effective in actually preventing cervical cancer. • pain, swelling, redness, itching, bruising, bleeding, and a lump where you got the shot • headache
A total of 7,802 people who received gardasil, made by merck and co. Although no vaccine is completely without side effects, the great majority of events have been mild and common, for example temporary soreness, swelling and redness at the site of the injection. The onset of symptoms was within 6 weeks after vaccination in 70% of the patients in whom the date of vaccination was known.
Gardasil is a human papillomavirus vaccine.gardasil is a sterile preparation for intramuscular injection and contains purified inactive proteins from hpv types 6, 11, 16, and 18. Very common side effects of the hpv vaccine. Pain, swelling, or redness where the shot was given;
The most common side effects seen with gardasil 9 are: Many of the reported events (such as headache, or feeling dizzy or unwell) may be equally common in people of the same age who have not received the vaccine. Maternal toxicity or adverse effects on offspring were not observed.
And pain, swelling, or redness in the arm where the shot was given. Common gardasil 9 side effects may include: More than 1 in 10 people who have the gardasil or gardasil 9 hpv vaccine experience:
Applies to human papillomavirus vaccine: Digging for data in vaers, the vaccine adverse event reporting system, in an attempt to show some relationship between report adverse events and gardasil is a form of “dumpster diving” for data. Report an adverse event using the vaers online form or the downloadable pdf.
These mild side effects may occur more often after gardasil 9 vaccination than after gardasil. They examined 2,500 cases and found 617 (25%) cases to be serious. Do not let your child be at risk without you knowing.
Fainting is more common among adolescents receiving the gardasil vaccine than in other kinds of vaccinations. When i originally wrote my gardasil. Inc., have reported adverse events to the cdc's vaccine adverse event reporting system (vaers) between june 8, 2006, and april.
Gardasil 9 protects against nine types. While the findings of some studies support the hypothesis that accidental intravenous vaccine administration caused these effects, these results were obtained in small. Women and girls who received gardasil 9 reported higher rates of swelling and redness where the shot was given than those who received gardasil.
Rr 0.93 (95% ci 0.72, 1.21) gardasil® versus control vaccine: Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. Intramuscular suspension general the most common adverse events were injection site reactions, fatigue, headache, and myalgia.
Rate of serious adverse events between gardasil® and placebo. Vaers, a passive reporting system, is barely more than an anecdotal reporting system, not scientific. The vaccine contains proteins that are similar to each of.
[5] patients aged ≥6 months were enrolled when seeking outpatient medical care for an ari. Low ve was anticipated due to.
Flu This Year's Vaccine Is Worse Than We Thought ABC News
Methods we enrolled patients 6 months of age or older who presented with acute respiratory illness at ambulatory care clinics in geographically diverse u.s.
Flu vaccine effectiveness 2015. Age group (years) influenza positive total influenza positive (% vaccinated) influenza negative total influenza negative (% vaccinated) adjusted ve % adjusted 95% ci; A systematic review of randomised controlled trials and observational studies 110 loeb et al. Preferential use of laiv among young children was not supported.
Influenza vaccine effectiveness for live attenuated influenza vaccines in children, against influenza a or b viruses; Despite comparatively poor health status among inpatients, influenza vaccination was effective in preventing hospitalizations associated with influenza. A canadian protocol now used globally reveals the flu shot doesn't work as well as scientists once believed.
Study results of vaccine effectiveness can vary based on the study design, the outcome. (healthday)—this season's flu vaccine may do little to prevent infection with the main circulating virus strain because the strain has changed since the vaccine was developed, a new study suggests. Vaccine effectiveness against a (h1n1)pdm09 among children was 63% (95% ci, 45 to 75;
Reported vaccine effectiveness (ve) estimates from ambulatory care settings were markedly decreased. 63 percent for influenza b and. Flu ve methods have been published previously.
Because h3n2 has been the vastly predominant flu type this year, this mismatch has been blamed for low vaccine effectiveness. Influenza vaccine effectiveness in adults and children in primary care in the uk: We assessed influenza vaccine effectiveness (ve) for the 2014/15 and 2015/16 seasons in israel, for the first time.
Adults, hospitalized at 2 hospitals in southeast michigan for acute respiratory illnesses, defined by admission. Morbidity and mortality weekly report. Influenza vaccine effectiveness for all vaccine types, against influenza a (h3n2) viruses;
A total of 3278 children were recruited from 13 selected nursery schools among 24 nursery schools in suzhou. These vaccine effectiveness (ve) studies regularly assess the value of flu vaccination as a public health intervention. A change in the h3n2 vaccine strain had been expected, since most of the circulating h3n2 viruses in the united states and a number of other countries have not matched well with the vaccine.
Age group (years) influenza positive total influenza positive (% vaccinated) influenza negative total influenza negative (% vaccinated) adjusted ve % adjusted 95% ci; P<0.001) for the inactivated vaccine, as compared with. We have updated this blog on 10/09/2015 to take account of the end of season flu vaccine effectiveness data for the 2014/15 flu season.
A systematic review 94 leung et al. Cdc conducts studies to measure the benefits of seasonal flu vaccination each flu season to help determine how well flu vaccines are working. 9882 patients with laboratory results were included of whi ch 2415 (24.4%) were positive for influenza, including
Every year international experts make important judgements about the likely flu viruses that will be circulating during the winter months in the northern hemisphere. Cdc’s adjusted overall ve estimate against influenza a and b viruses for all ages was 23%.
Age group (years) influenza positive total influenza positive (% vaccinated) influenza negative total influenza negative (% vaccinated) adjusted ve % adjusted 95% ci; Sax , 1 joe suyama , 3 emily bobyock , 1 charles r.
National EarlySeason Flu Vaccination Coverage, United
These interim ve estimates indicate that influenza vaccination reduced the risk for outpatient medical visits by almost half.
Flu vaccine 2016 effectiveness. Jackson , 6 manjusha j. P<0.001) for the inactivated vaccine, as compared with −19% (95% ci, −113 to 33; Vaccine effectiveness is an estimate of the likelihood that a vaccine prevents influenza infection when used in everyday practice.
Influenza activity is likely to continue for several more weeks in the united states, and vaccination efforts should continue as long as influenza viruses are circulating. Sparse numbers didn't allow estimating ive in all. According to data from the u.s.
Of 9311 enrollees with complete data, 7078 (76%) were influenza negative, 1840 (19.8%) were positive for influenza a (a/h3n2, n = 1817), and 395 (4.2%) were positive for influenza b (b/yamagata, n = 340). Influenza vaccine effectiveness for all vaccine types, influenza b/victoria lineage viruses ; Vaccination prevented around 1 in 4 hospitalisations with influenza.
The 2016/17 season saw early influenza a(h3n2) virus circulation with care home outbreaks and increased excess mortality particularly in those 65 years or older. Effectiveness of the influenza vaccine in preventing admission to hospital and death in people with type 2 diabetes. Public health england ( phe) has today (wednesday, 18 july 2018) published data on the effectiveness of the flu vaccine in the 2017 to 2018 season.
Our findings were consistent with expected influenza vaccination effectiveness in seasons when the vaccine matched or mismatched circulating viruses. Balasubramani , 1 mary patricia nowalk , 2 theresa m. In children are for live attenuated influenza vaccine only.
Introduction the united kingdom is in the fourth season of introducing a universal childhood influenza vaccine programme. Overall vaccine effectiveness by laboratory confirmed rt pcr showed mild protection of ∼30.0% for any influenza and influenza a but ve was higher as 50.2% against influenza b. Vaccine effectiveness against a (h1n1)pdm09 among children was 63% (95% ci, 45 to 75;
The global influenza hospital surveillance network is an international platform whose primary objective is to study severe cases of influenza requiring hospitalization. Age group (years) influenza positive total influenza positive (% vaccinated) influenza negative total influenza negative (% vaccinated) adjusted ve % adjusted 95% ci; To establish how well influenza vaccines work each season, influenza vaccine effectiveness is measured in observational studies.
Influenza vaccine effectiveness for live attenuated influenza vaccines in children, against influenza a or b viruses; Final estimates will be published later in summer 2016. Influenza vaccine effectiveness among outpatients in the us influenza vaccine effectiveness network by study site 2011‐2016 goundappa k.
We assessed the vaccine effectiveness (ve) of inactivated influenza vaccine (iiv) in children 6 months to 15 years of age in 2015/16 season. A 2018 study showed that from 2012 to 2015, flu vaccination among adults reduced the risk of being admitted to an intensive care unit (icu) with flu by 82 percent. The data show that overall, flu vaccine was 15%.
Martin , 5 arnold s. Virus characterisation data indicated emergence of genetic clusters within the a(h3n2) 3c.2a. A new report from the centers for disease control and prevention (cdc) details just how effective the flu shot has been so far this season.
63 (33) 5040 (52) 56% (23 to 75) Age group (years) influenza positive total influenza positive (% vaccinated) influenza negative total influenza negative (% vaccinated) adjusted ve % adjusted 95% ci; Monto , 5 michael l.
In this cohort of patients with type 2 diabetes, influenza vaccination was associated with reductions in rates of admission to hospital for specific cardiovascular events. Influenza vaccine effectiveness for all vaccine types, against influenza a (h3n2) viruses;

