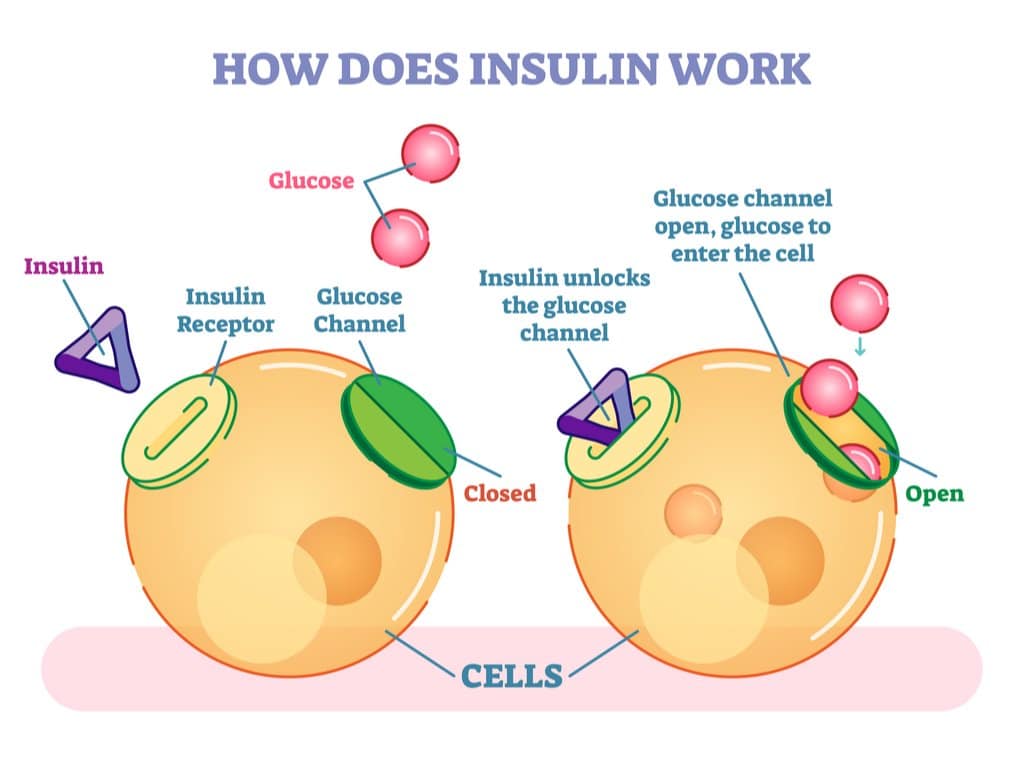
Insulin generally reduces the blood glucose level by depositing the glucose in the liver and muscles as glycogen. The following steps show the different changes in the body before, during and after a meal is eaten:
The Role of Insulin in the Body 99 My Health Tips
Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite effect by promoting widespread catabolism, especially of reserve body fat.
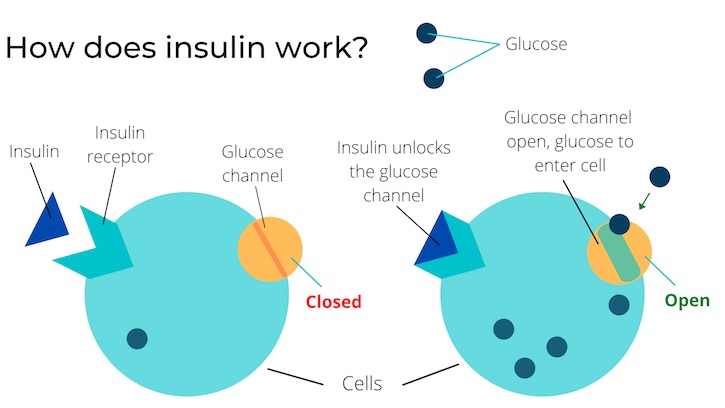
What effect does insulin have on the body. “insulin causes weight gain for as long as a person uses it.” insulin might increase weight at first, but this is not an ongoing effect. Not only does it drive most cells to preferentially oxidize carbohydrates instead of fatty acids for energy, insulin indirectly stimulates accumulation of fat in adipose tissue. By monitoring glucose levels, amino acids, keto acids, and fatty acids circulating within the plasma, beta cells regulate the production of insulin accordingly.
Insulin is an anabolic hormone that elicits metabolic effects throughout the body. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules inside the cells. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone that are released from the beta cells of the pancreas.
Insulin regulates the metabolism of carbohydrate and proteins in the body. Insulin therefore helps cells to take in glucose to be used for energy. Both help manage blood glucose levels.
Insulin is grouped according to how long it works in the body. If the body has sufficient energy, insulin. Your insulin spikes to regulate your blood sugar.
Excess glucose will also accumulate in the kidney and tubule lumen, then retains water causing increased urine. One of insulin's major functions is to prevent the use of fat as an energy source in the body. Insulin is secreted by the pancreas which regulates the blood glucose level in the blood.
If you have recently been prescribed insulin, or have switched to a new type of insulin, you may be concerned about the side effects. Insulin regulates the amount of blood sugar level in the body. Scar tissue will significantly derail absorption.
And a little while later you get that familiar sugar crash. Once you eat glucose, your body releases insulin, a hormone from your pancreas, dr. Insulin allows the cells in the muscles, fat and liver to absorb glucose that is in the blood.
34 insulin stimulates glucose uptake, promotes lipogenesis while suppressing lipolysis, and hence free fatty acid flux into the bloodstream. The pancreas releases insulin in response to high blood glucose level, which allows the cells to remove the glucose from the blood and use it for providing energy to the body instead. Over time, scar tissue can build up, and entire areas of your body can become basically “unusable” for injections or infusion sites.
Increases in muscle glut4 protein content contribute to this effect, and in addition it has been hypothesized that the depletion of muscle glycogen stores with exercise plays a role herein. Lack of insulin increases glucose in the blood, because the cells are unable to absorb the glucose. The insulin regulates the blood glucose level.
The insulin's job is to absorb the excess glucose in the blood and stabilize sugar levels. Its function is to allow other cells to transform glucose into energy throughout your body. Other notable effects of insulin
Insulin also affects other metabolic processes, such as the breakdown of fat or protein. Without insulin, cells are starved for energy and must seek an alternate source. Recent studies have accordingly shown that acute exercise also enhances insulin stimulated glut4 translocation.
I have had times when i know i’ve hit scar tissue, and a shot of insulin will have no effect for two hours, shooting my blood glucose into the stratosphere. Normal blood glucose concentration in. Deficiency of insulin causes diabetes in the individual and needs insulin injection.
People with diabetes often receive insulin injections. Deficiency of insulin causes diabetes in the individual and needs insulin injection. The body first needs to adapt to insulin supplementation.
The glucose serves as energy to these cells, or it can be converted into fat when needed. People with diabetes often receive insulin injections. Beta cells are responsible for insulin synthesis.
The insulin injection maintains the blood glucose level. Insulin regulates the metabolism of carbohydrate and proteins in the body. If you have type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesn’t make insulin.
Pancreas is both an exocrine as well as an endocrine gland What effect does insulin have on the body? Similarly, you may be looking for information for a friend or family member.
The effects of insulin on the body. In diabetic people, enough insulin is not produced by the pancreas as a result glucose level increases in the blood which is called hyperglycemia. In the pancreas, exocrine tissue known as the islets of langerhans contain beta cells.
Insulin is a hormone that your body makes to help move sugar (glucose) from your body’s bloodstream into your cells. In doing so, it also pushes the body to take glucose out of the blood and store it. The insulin regulates the blood glucose level.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas. Insulin helps control blood glucose levels by signaling the liver and muscle and fat cells to take in glucose from the blood. The insulin injection maintains the blood glucose level.
People with type ii diabetes are making insulin in their bodies, but their bodies do not respond to it or respond well, that's why they need insulin injections so their bodies can use glucose for energy (insulin makes glucose blood levels down) sikringbp and 5 more users found this answer helpful. Because glucose is the main source of injury, the body won't have enough fuel to burn and a person may feel more tired than usual. What effect does insulin have on the body?
You might also be experiencing side effects and not know where they are coming from. It's a hormone which is secreted by the pancreas. It is estimated that adipose tissue accounts for about 10% of insulin stimulated whole body glucose uptake.
Problems with insulin production or use Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. Your cells use the sugar as fuel for your body.

The Effects of Insulin Resistance on the Body LIWLI

Physiology of Insulin and Glucagon Insulin, Protein

Adropin has minimal beneficial effects on wholebody

Controlling Insulin and blood sugar to assist with weight loss

Clinical Trials, Triumphs, and Tribulations of Glucagon
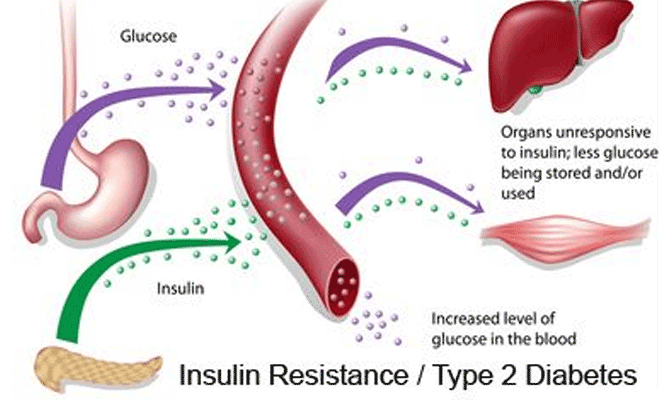
Insulin Resistance Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis

Insulin is a major regulator of metabolism and organ
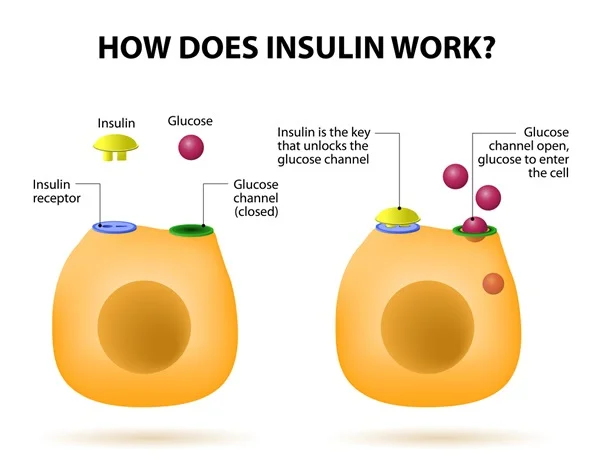
Insulin's role in the human body