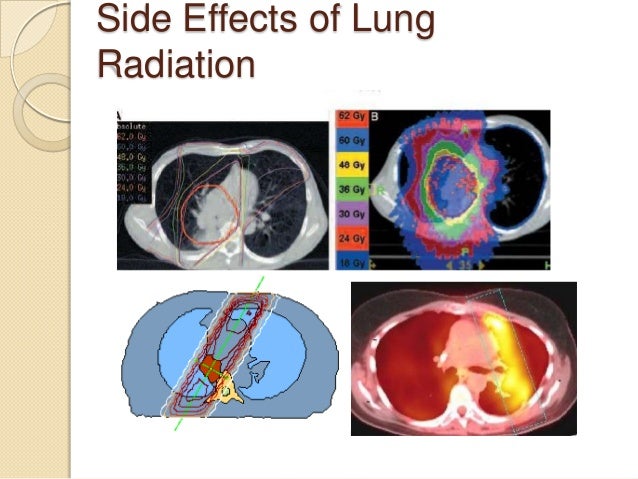
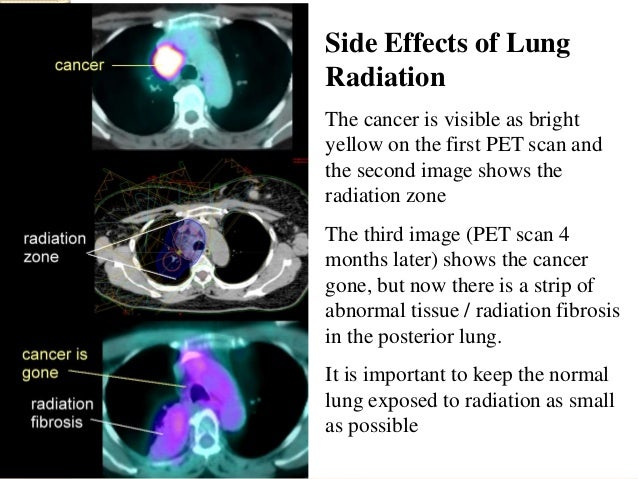
Side effects of radiation therapy. The primary function of this therapy is to destroy the cancerous cells present in the lungs.

Siding Windows Doors Side Effects From Lung Cancer
And get plenty of rest.

Radiation therapy for lung cancer side effects. Radiotherapy to the lung can cause side effects such as tiredness, sore skin and a cough. Some people feel fine, while others are uncomfortable. When chemotherapy is given with radiation, the side effects may be worse.
Some common side effects of radiation therapy used for lung cancer are: Most lung cancers are treated with radiation therapy, often in high doses. Radiation therapy to the chest may damage your lungs, which might cause a.
Common side effects of radiation therapy for lung cancer can include: There are also some side effects specific to your cancer type. Common side effects depend on where the radiation is aimed and can include:
Fatigue coughing side effects are minimal and usually go away quickly according to the maker of cyberknife: Radiation exposure to healthy lung tissue and nearby organs is limited or eliminated, reducing side effects like difficulty breathing. People may have mild to severe symptoms, however, there have been cases where people did not have any adverse.
These are commonly reported side effects across all the cancers. The reason radiation therapy works is because it damages the dna of cells, he says. You may develop a dry cough after treatment due to inflammation of the lung from radiation.
Earaches or difficulty hearing if the ear is in the treatment area; Radiation therapy is given to patients to reduce the size of tumor. Other side effects depend on the part of the body that is.
Radiation therapy has side effects because it not only kills or slows the growth of cancer cells, it can also affect nearby healthy cells. Intensity modulated radiation therapy (imrt): If your cough does not get better you should contact your provider.
Possible side effects of radiation therapy for nsclc. Radiation therapy plays an important role in the management of both limited stage and extensive stage small cell lung cancer. Most side effects go away within two months but late side effects may occur.
Side effects of radiation therapy include nausea and vomiting, skin problems, and tiredness. However, there are several ways a person can reduce the severity of these side effects. Most of these side effects go away after treatment, but some can last a long time.
Sometimes, it is the only treatment suggested for lung cancer. Rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells, are more affected by radiation therapy than normal. Radiation therapy may cause inflammation of the lungs, known as radiation pneumonitis.
This may cause shortness of breath, a cough or both. Some of the side effects of radiation depends on the type of cancer and the area of the body affected. Many people who get radiation therapy experience fatigue.
Cyberknife side effects for lung cancer cyberknife treatment can be done in conjunction with chemotherapy or on its own, depending on each patient and the treatment plan suggested. Your doctor can prescribe medication with therapies to help with these side effects. Side effects of radiation therapy will depend mainly on the size of the area being treated, the specific area or organs being treated, the total dose of radiation, the treatment schedule and if radiation therapy is being given with chemotherapy.
Common physical side effects of radiation therapy include: Radiation therapy can also affect healthy tissue near the tumor site, and may cause redness. Some side effects may occur.
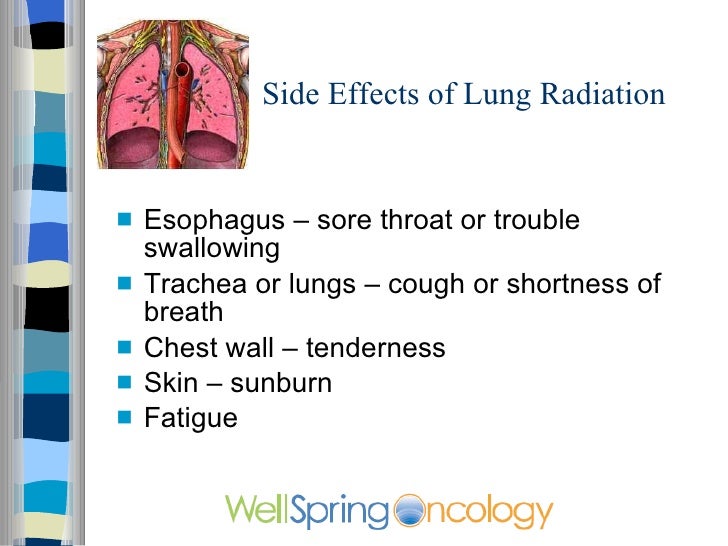
Its effects may vary individually. These effects tend to start a week after the radiotherapy begins. Skin blistering or dryness, sore throat, trouble swallowing, coughing and shortness of breath are all common.
If you are going to get radiation therapy, it’s important to ask your doctor about the possible side effects so you know what to expect. Loss of appetite and weight loss Generally speaking, the most common side effects of lung cancer chemotherapy include:
Reduced appetite and weight loss One of the most common side effects of radiation therapy is fatigue, a feeling of exhaustion. Side effects of radiotherapy | lung cancer | cancer research uk
Possible side effects of radiation therapy. Some people who receive radiation therapy experience dryness, itching, blistering, or peeling. The radiation from the pellets is designed to kill the cancer and limit effects on the nearby healthy tissues.
Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy (sabr) is a highly advanced, sophisticated, and safe treatment which allows patients with early stage lung cancer to be treated effectively without invasive procedures and with excellent clinical outcomes. Side effects from radiation therapy may vary from one patient to the next because the direction the beam travels through each person’s body may be different. Side effects will depend on factors such as the treatment area, total dose of radiation, type of radiation therapy used, and whether chemotherapy is given at the same time (chemoradiation).
Side effects of radiation therapy to the head and neck may include: For limited stage disease, there has been a trend toward reduced size of thoracic radiation fields, which has the potential to. Side effects vary with type of cancer.
Commonly, radiation side effects lessen and disappear after treatment ends. Changes to the voice, such as hoarseness, if. The side effects of radiation treatments on lung cancer depend on the type of radiation and the location where treatment is administered.
Side effects of lung cancer radiation treatment. Side effects from cyberknife can include:
Intensity modulated proton therapy shows promise for lung
Side Effects of Lung Radiation
/iStock_000026209728_Large-56a5c5875f9b58b7d0de6a95.jpg)
Lung Cancer Skin Rash Pictures Steve

Side Effects Of Radiation Therapy For Lung Cancer All
Today's radiation treatments offer better success, fewer

Side effects of radiation therapy Why me? Atlas of Science

Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy In NonSmall Cell