Another important consideration is that, as blood glucose concentrations fall, insulin secretion ceases. It lowers blood glucose by telling cells to absorb and use it.
Figure 3 Insulin Action in Brain Regulates Systemic
Insulin allows the cells in the muscles, fat and liver to absorb glucose that is in the blood.

What is the effect of insulin. (ii) decreased blood glucose concentration and. This is the most important consequence of too much insulin. This has helped us understand a product’s carbon footprint, or the sum of all emissions across a product’s life.
The glucose serves as energy to these cells, or it can be converted into fat when needed. Over time, blood glucose levels above the normal range can damage your eyes, kidneys and nerves, and can also cause. If your cells’ insulin sensitivity is low, they won’t absorb enough glucose — you have insulin resistance, which can lead to type 2 diabetes.
Drowsiness, unsteady movements, slurred speech, etc. Hypoglycemia occurs as a result of. Insulin also assists in breaking down fats or proteins for energy.
Insulin has several effects that lead to fat storage in adipose tissue. Insulin triggers the uptake of glucose, fatty acids and amino acids into liver, adipose tissue and muscle and promotes the storage of these nutrients in the form of glycogen, lipids and protein respectively. Insulin may exert positive or negative effects on the neurons expressing ghrh and ss and somatotropes under healthy and pathological conditions including obesity and diabetes.
However, taking insulin can be tricky. After this, the effect gradually wears off and blood glucose levels rise. First, insulin increases the utilization of glucose by most of the body’s tissues, which automatically decreases the utilization of fat, thus functioning as a fat sparer.
Add to that the fact that a hypo can look a lot like being drunk: Insulin has three basic effects on carbohydrate metabolism: Insulin lowers blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake primarily by skeletal muscle cells and fat, and by inhibiting glucose production and release by the liver.
After the first isolation of insulin from the pancreas in the early 1920s, visscher and muller were probably the first to attribute a positive inotropic effect to insulin in an isolated heart preparation. Insulin is a hormone released by pancreatic beta cells in response to elevated levels of nutrients in the blood. With all doses, large and small, the onset of action and the time to peak effect is similar, the duration of insulin action is, however.
When glucose is at its lowest level, the effect of the insulin is said to have reached its ‘peak’. For the past 25 years, novo nordisk has looked at the environmental impact of our products at all stages of its life cycle. Insulin helps control blood glucose levels by signaling the liver and muscle and fat cells to take in glucose from the blood.
(iii) increased glycogen stores in the tissues. Insulin is a hormone that rises when blood glucose rises. “insulin causes weight gain for as long as a person uses it.” insulin might increase weight at first, but this is not an ongoing effect.
When you take insulin it acts to reduce the level of glucose in your blood. Insulin therefore helps cells to take in glucose to be used for energy. Our ambition for our company and our products (including your insulin pen) is to have zero environmental.
If the body has sufficient energy, insulin. Insulin also affects other metabolic processes, such as the breakdown of fat or protein. 1 however, data on the effects of insulin on cardiac function and metabolism remain conflicting.
Glucose and lipid levels in circulation and dietary habits may. Insulin also helps balance your blood glucose levels. Several aspects of the effect of insulin on myocardial function and metabolism have been.
The insulin receptor and its direct substrates. The body first needs to adapt to insulin supplementation. However, insulin also promotes fatty acid synthesis.
Insulin inhibits lipolysis (breakdown of fat), proteolysis (breakdown of proteins), and gluconeogenesis (manufacture of glucose). The american diabetes association defines hypoglycemia as a glucose reading less than or equal to 70 mg/dl. A delicate balance of insulin regulates blood sugar and many processes in the body.
Once glucose is in your bloodstream, insulin signals cells throughout your body to absorb the sugar and use it for energy.
The Inhibitory Effects of Insulin on Hepatic Glucose

1 Partial list of insulin's effects on whole body

Schematic diagram of the effects of insulin resistance on

Schematic representation showing the effects of insulin on
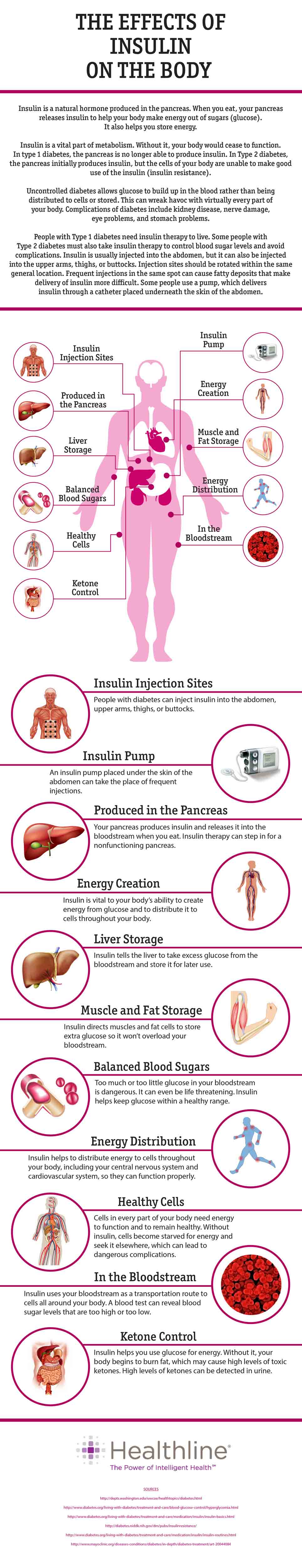
11 Effects of Insulin on the Body

Diabetes Insulin and its metabolic effects

“Effects of Insulin Deficiency . . .

Metabolic effects of IGF1, GH, and insulin under

11 Effects of Insulin on the Body
Effects of TZDs on the three primary insulinresponsive