Schizophrenia is a chronic progressive disorder that has at its origin structural brain changes in both white and gray matter. This suggests that schizophrenia affects the brain regions which control echoic or aud itory sensory memory outside the prefrontal cortex.

STOP THE STIGMA! Schizophrenia
But our latest research shows that organs, other than the.
Schizophrenia effect on brain. Andreasen's team learned from the brain scans that those affected with schizophrenia suffered the most brain tissue loss in the two years after the first episode, but then the damage curiously. A new study reveals people with schizophrenia often have an over active immune system and other physical disorders. Both schizophrenia and multiple personality disorder chiefly affect biographical or episodic memory , leaving semantic and procedural memory largely accessible (to all of the person’s identities).
Schizophrenia is not as common as other mental diseases it can be very This article explores how meth affects the body and brain and how prolonged use of meth can lead to paranoia and schizophrenia, as well as treatment. Andreasen’s team learned from the brain scans that those affected with schizophrenia suffered the most brain tissue loss in the two years after the first episode, but then the damage curiously plateaued—to the group’s surprise.
9 habits that may reduce your risk for developing alzheimer's. Andreasen’s team learned from the brain scans that those affected with schizophrenia suffered the most brain tissue loss in the two years after the first episode, but then the damage curiously plateaued—to the group's surprise. Extreme poverty, stressful surroundings, childhood trauma, and exposure to viruses or nutritional problems before birth are some environmental factors that are associated with an increased risk of schizophrenia.
People demonstrating the worst brain tissue losses also tend to show the worst symptoms. Although schizophrenia affects men and women with equal frequency. That’s because brain areas that run on dopamine may become overactive.
For individuals with schizophrenia, these findings suggest environmental stressors may alter the balance in brain receptors that are controlled by antipsychotic drugs. Schizophrenia is considered a disorder of the mind, influencing the way a person thinks, feels and behaves. Schizophrenia is associated with changes in the structure and functioning of a number of key brain systems, including prefrontal and medial temporal lobe regions involved in working memory and declarative memory, respectively.
This mental health condition affects the structure and functioning of a few essential systems in the brain. Straightforward submission service, including a free language check on your manuscript. Schizophrenia could be physically changing the body, not just the brain.
These areas are known to be important for coordination of thinking and judgment. Schizophrenia affects roughly 3.5 million people, or about one percent of the u.s. Symptoms of schizophrenia include delusions, disorganized speech, hallucinations, trouble thinking, and extreme lack of motivation.
Meth (methamphetamines) is a highly addictive and powerful drug that stimulates your central nervous system, giving the body increased energy and feelings of euphoria. Schizophrenia is likely a side effect of our brain’s complex evolution this discovery could lead to not only a better understanding of our evolution but to new treatment options for. Researchers say schizophrenia should not be considered to be just a disorder of the mind, as schizophrenia can also impact other organs.
If antipsychotics are needed for symptom control and relapse prevention yet with increasing dosage there is a risk of atrophic brain changes, the need to optimize drug dosing would be increased, emphasizing lower effective dosages rather than raising dosage to the level just below a significant side effect threshold. Also, the timing of exposure affects important structural brain abnormalities prominent in schizophrenia such as ventriculomegaly, with only the earlier exposure producing this abnormality 82. Andreasen’s study, published in the american journal of psychiatry, documented brain changes seen in mri scans from more than 200.
Early brain development and is expressed as a combination of psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions and disorganization and motivational and cognitive dysfunctions. People with schizophrenia have up to 25% less volume of gray matter in their brains, especially in the temporal and frontal lobes. It alters brain chemistry and brain form to produce the different behavior in those afflicted with the problem.
Differences in brain structure, function, and neurotransmitter interactions can contribute to the development of. Schizophrenia is a disease that affects the brain. In schizophrenia, dopamine is tied to hallucinations and delusions.
Schizophrenia is another disease that occurs inside the brain that features lasting structural and functional changes. Schizophrenia is a profound and complex brain condition that affects how people relate to the world around them. Schizophrenia affects your body, not just your brain.
It is likely that these changes begin prior to the onset of clinical symptoms in cortical regions, particularly those concerned with language processing.
Schizophrenia Brain Impact of Schizophrenia on the Brain

Is Schizophrenia Really a Brain Disease Blogs Science
Schizophrenia is an "unwanted side effect" of complex
What places in the human brain does schizophrenia affect

Schizophrenia a side effect of human development
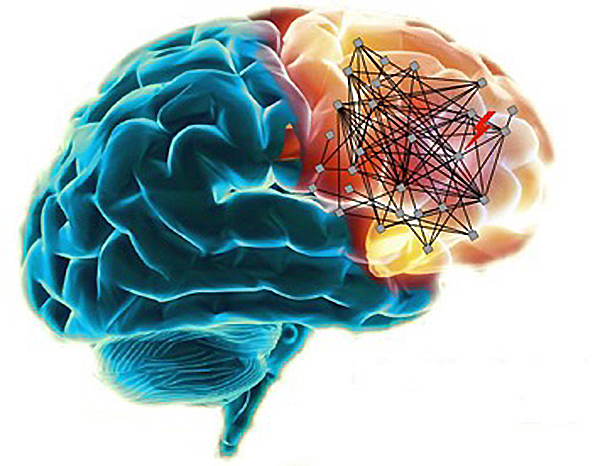
Mutated Genes in Schizophrenia Map to Brain Networks
Schizophrenia Summing it Up Emotion, Brain, & Behavior
Schizophrenia Fact and Schizophrenia

Mapping adolescent brain change reveals dynamic wave of

New study finds evidence for reduced brain connections in