Symptoms of schizophrenia include delusions, disorganized speech, hallucinations, trouble thinking, and extreme lack of motivation. Schizophrenia is a profound and complex brain condition that affects how people relate to the world around them.

Bioengineers at Work Schizophrenia A Mental Disease with
Schizophrenia is considered a disorder of the mind, influencing the way a.

Schizophrenia effects on brain. According to the world health organization, schizophrenia affects over 21 million people across the globe. Andreasen’s team learned from the brain scans that those affected with schizophrenia suffered the most brain tissue loss in the two years after the first episode, but then the damage curiously plateaued—to the group’s surprise. Ad a forum on the treatment of smoking cessation, focusing on observational studies.
When schizophrenia is active, symptoms can. Correspondingly, they can not process inputs to the same degree. While the cause of this serious mental health disorder is not completely clear, research overwhelmingly infers that schizophrenia is a biological disease of the brain.
Moreover, we reviewed studies examining the longitudinal effects of medication on brain structure in patients with schizophrenia. Atrophy (loss of brain cells/shrinkage) of the hippocampus is among the most notable changes in the brains of people with schizophrenia. It is likely that these changes begin prior to the onset of clinical symptoms in cortical regions, particularly those concerned with language processing.
It alters brain chemistry and brain form to produce the different behavior in those afflicted with the problem. People with schizophrenia may believe others are reading their minds, have unusual sensory experiences such as hearing things others don’t hear or seeing things others don’t see, or believe others are after them to do them harm. That’s because brain areas that run on dopamine may become overactive.
Andreasen’s team learned from the brain scans that those affected with schizophrenia suffered the most brain tissue loss in the two years after the first episode, but then the damage curiously plateaued—to the group's surprise. This kind of brain has been found in affected people who went through pet scans or mri scans in studies made by professionals who are interested in brain structures. This mental health condition affects the structure and functioning of a few essential systems in the brain.
The schizophrenia brain is when something is amiss in the brain development that may cause unusual symptoms that can be described as this kind of psychological disorder. Their outputs consequently are not the responses expected. These problems cause the symptoms of schizophrenia, which include hallucinations, delusions, disordered thinking, and unusual speech or behavior.
In the largest study of its kind to date, 160 scientists from 27 institutions worldwide set out to examine how schizophrenia. Kraepelin’s use of the term “dementia praecox” for the condition we now know as schizophrenia encouraged the view that his patients had a progressive decline in behavioral function associated with (and probably caused by) progressive changes in brain anatomy and function over the course of illness. Andreasen's team learned from the brain scans that those affected with schizophrenia suffered the most brain tissue loss in the two years after the first episode, but then the damage curiously.
There is a definite deficit present because a schizophrenic is not as aware of the surrounding world. The american psychiatric association reports that “schizophrenia is a chronic brain disorder that affects less than one percent of the u.s. Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves.
If left untreated, the symptoms of schizophrenia can be persistent and disabling. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality, which causes significant distress for the individual, their family members, and friends. Schizophrenia is a severe, disabling disease of the brain that causes individuals to view the world in unusual ways.
In schizophrenia, dopamine is tied to hallucinations and delusions. A person with the disease develops differently than a normal person. Schizophrenia is a chronic progressive disorder that has at its origin structural brain changes in both white and gray matter.
Our primary aim was to determine whether nicotine improves cognitive function by facilitating activation of brain regions mediating task performance or by facilitating functional. Schizophrenia is a disease that affects the brain. Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves.
However, the reductions in dendritic spines and synapse density noted in postmortem studies of patients with schizophrenia are localized primarily to glutamatergic pyramidal cells , and ltp and other processes dependent on nmda receptors are critically involved in the synaptic pruning that characterizes normal adolescent brain development , thus. They may hear voices other people don’t hear. Studies also suggest that the hippocampus (a structure in the temporal lobe that influences learning and memory) also presents differently in people with schizophrenia.
Nicotine in tobacco smoke can improve functioning in multiple cognitive domains. Join leading researchers in the field and publish with us. Superior temporal and inferior frontal regions) in those individuals who later made transition to.
High rates of smoking among schizophrenic patients may reflect an effort to remediate cognitive dysfunction. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality.

Understanding of the brain Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is an "unwanted side effect" of complex
What places in the human brain does schizophrenia affect

Mapping adolescent brain change reveals dynamic wave of
Schizophrenia Summing it Up Emotion, Brain, & Behavior
What Causes Schizophrenia? Psychic Monday
Schizophrenia Brain Impact of Schizophrenia on the Brain
On the edge of reality. Schizophrenia and psychosis
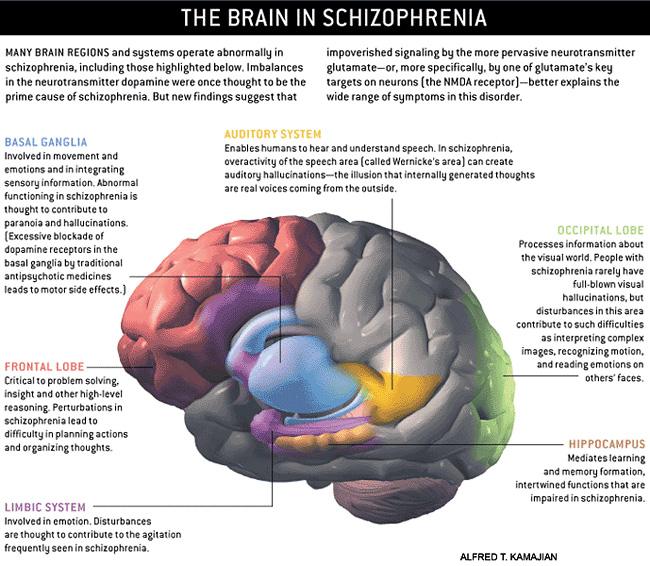
Schizophrenia And The Risks Of Substance Abuse
How changes in the brain's wiring impact on schizophrenia